Principal Bacterial STIs: <br />Gnorrhea
18

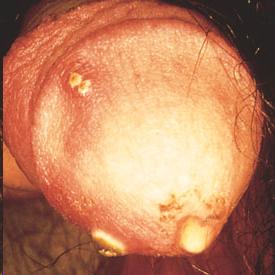
Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported notifiable disease in the United States and 700,000 people are infected annually. Gonorrhea is transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person. The organism thrives in the warm, moist environment provided by the mucous membranes lining the mouth, throat, vagina, cervix, urethra, and rectum. Though some infected men may be asymptomatic, men tend to experience the symptoms of gonorrhea more readily than women. It is popularly referred to as "the clap" or "the drip," because early symptoms include a watery discharge from the penis or increased vaginal discharge. Other symptoms include burning and pain during urination. If untreated, the disease soon produces other symptoms, such as thick yellow or greenish discharge, increasing discomfort or pain with urination, and painful or swollen testicles.
Up to 80% of women with gonorrhea show no symptoms or very mild symptoms, which they tend to ignore. Untreated gonorrhea can cause sterility in both sexes, ectopic pregnancy, prostate damage, epididymitis, scarring of the urethra in men, and testicular pain. It is diagnosed using a urine or sample from the infected body part. Gonorrhea is curable with several antibiotics. However, emergence of drug-resistant strains of gonorrhea is making successful treatment more difficult.
Image: McGraw Hill