Gender Variations

18
Two syndromes resulting from erroneous chromosomal patterns may result in gender confusion. We will discuss:
Turner syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome In both of these, the body develops with some marked physical characteristics of the other sex.
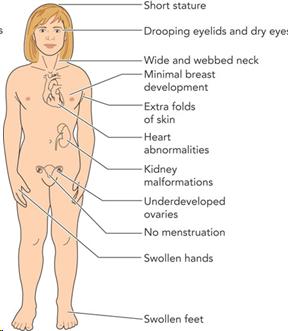
Turner syndrome is described as females who lack a chromosome and are described as XO rather than XX or XY. The individual has a female external appearance but no ovaries. Therfore, changes initiated by ovarian hormones cannot take place. The body does not gain a mature look or height and menstruation cannot occur. These individuals may have academic problems and poor memory and attention. Treatments include hormonal therapy and assisted fertility. The hormonal therapy includes androgen, estrogen, and human growth hormone therapy, replacing the hormones to produce adolescent changes. Unfortunately, the female will likely remain infertile.
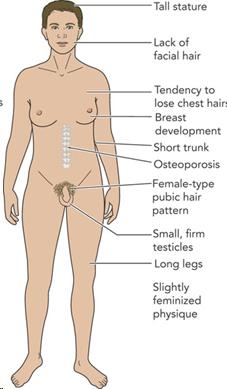
Klinefelter syndrome is related to males. These individuals are males who have an extra X chromosome. For example, the could be XXY or XXXY or XXXXXY rather than XY. The testes of these males are small and firm, and they also have some female physical traits. Many men with Klinefelter syndrome are never diagnosed. The physical traits include tallness, breast development, sparse body hair, and/or a small penis and testes. They tend to exhibit learning disabilities and also have lower testosterone levels which cause low sex drive, the inability to experience erections, and infertility. Treatment includes testosterone replacement. This prevents osteoporosis, maintains physical energy, sexual functioning, and well-being, and in-vitro techniques can allow some to become a biological father.
Images from McGraw Hill Image Library