KIN122- Chapter 5
Table of Contents
- Chapter 5 The Power of Resistance Training: Strengthening Your Health
- Objectives
- Physical Activity Recommendations for Health
- Components of Health-Related Physical Fitness
- Benefits of Muscular Strength & Endurance
- Skeletal Muscle Groups Front and Back
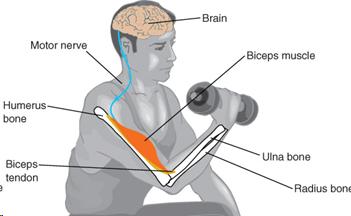
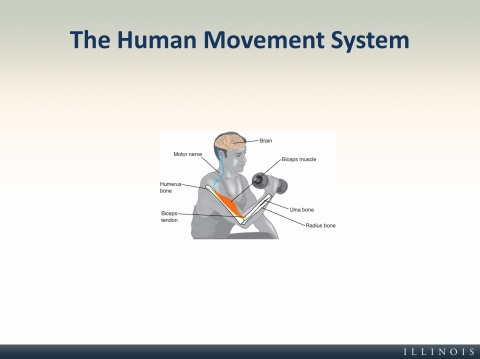
- The Human Movement System
- The Structure of Skeletal Muscle
- The Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction
- Muscle Fiber Types
- Dynamic Muscle Actions
- Definitions related to strength
- Four Factors Contribute to Muscle Strength and Size
- Types of Resistance Training
- Types of Dynamic Resistance Exercise (1)
- Dynamic Constant External Resistance (1)
- Dynamic Constant External Resistance (2)
- Types of Dynamic Resistance Exercise (2)
- Measuring muscular strength & endurance
- Designing Your Resistance Training Program (1)
- Designing Your Resistance Training Program (2)
- Designing Your Resistance Training Program (3)
- Sample Weight Training Programs
- Designing Your Resistance Training Program (4)
- Sources
Text and Images from Slide
The Human Movement System