Table of Contents
- Female & Male Sexual Anatomy Chapters 3 & 4
- Main Topics
- Embryonic-fetal Differentiation of the External Reproductive Organs
- Homologous Sexual Organs
- Male & Female Sex Organs: What Are They For?
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- External Female Genitalia With The Labia Drawn Apart (Vulva)
- Internal Female Sexual Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: External Structures
- Male Sex Organs: External Organs
- Male Sex Organs: External Organs
- Internal Side View of the Male Sex Organs
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male & Female Sex Organs: The Breasts
- Male & Female Sex Organs: The Breasts
- Male & Female Sex Organs: Anus
- Summary
Text and Images from Slide
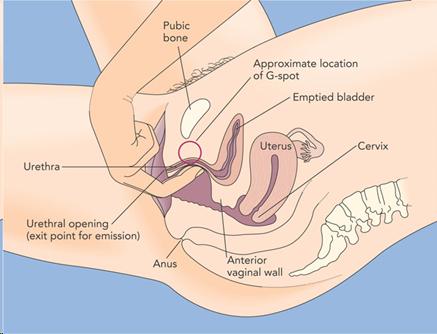
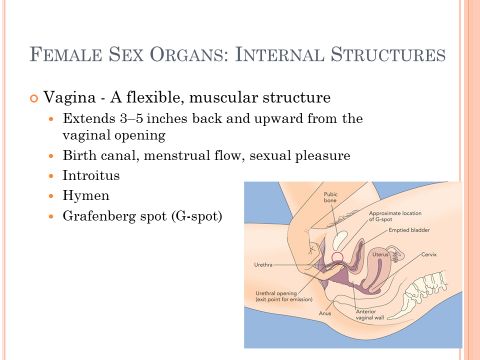
Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Vagina - A flexible, muscular structure
- Extends 3-5 inches back and upward from the vaginal opening
- Birth canal, menstrual flow, sexual pleasure
- Introitus
- Hymen
- Grafenberg spot (G-spot)
11