Table of Contents
- Female & Male Sexual Anatomy Chapters 3 & 4
- Main Topics
- Embryonic-fetal Differentiation of the External Reproductive Organs
- Homologous Sexual Organs
- Male & Female Sex Organs: What Are They For?
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- Female Sex Organs: External Structures
- External Female Genitalia With The Labia Drawn Apart (Vulva)
- Internal Female Sexual Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Female Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: External Structures
- Male Sex Organs: External Organs
- Male Sex Organs: External Organs
- Internal Side View of the Male Sex Organs
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male Sex Organs: Internal Structures
- Male & Female Sex Organs: The Breasts
- Male & Female Sex Organs: The Breasts
- Male & Female Sex Organs: Anus
- Summary
Text and Images from Slide
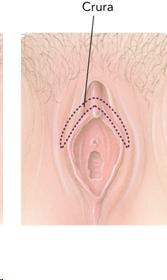
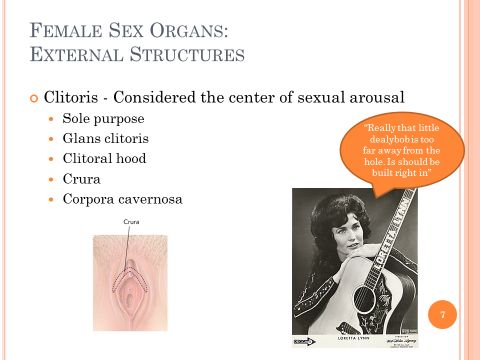
Female Sex Organs: <br />External Structures
7


"Really that little dealybob is too far away from the hole. Is should be built right in"
- Clitoris - Considered the center of sexual arousal
- Sole purpose
- Glans clitoris
- Clitoral hood
- Crura
- Corpora cavernosa